Evaluation AC3-11: Difference between revisions
m (Dave.Ellacott moved page Gold:Evaluation AC3-11 to Evaluation AC3-11 over redirect) |
|||
| (37 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
7) Jackson J.D., He S., Xu Z., Wu T., 2000, “CFD Quality and Trust – Generic Studies of Thermal Convection”, ''Technical Report HTH/GNSR/5029'', School of Engineering, Univeristy of Manchester. | 7) Jackson J.D., He S., Xu Z., Wu T., 2000, “CFD Quality and Trust – Generic Studies of Thermal Convection”, ''Technical Report HTH/GNSR/5029'', School of Engineering, Univeristy of Manchester. | ||
8) | 8) J.D. Jackson, Zeyuan Xu and Tian-Hua Wu, 2003, "On the influence of | ||
buoyancy on turbulence production and effectiveness of heat transfer | |||
in vertical flows", ''Turbulence, Heat and Mass Transfer'' '''4''' (published | |||
by Begell House, and edited by K. Hanjalic, Y. Nagano and M.J. | |||
Tummers), pp 837-844, Proceedings of the 4th International THMT | |||
Symposium, Antalya, Turkey, 12th - 17th October 2003. | |||
9) | 9) Jones, W.P., Launder, B.E., 1972, “The Prediction of Laminarization with a Two-Equation Model of Turbulence”, ''Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer'', '''15''', 301-314. | ||
10) | 10) Launder B.E., Sharma B.I., 1974, “Application of the Energy-Dissipation Model of Turbulence to the Calculation of Flow Near a Spinning Disc”, ''Letters in Heat and Mass Transfer'', '''1''', pp131-138 . | ||
11) | 11) Launder, B.E., 1986, “Low-Reynolds-Number Turbulence near Walls”, ''Report TFD/86/4'', Dept of Mechanical Engineering, UMIST. | ||
12) | 12) Leonard B.P., 1979, “A stable and accurate convective modeling procedure based on quadratic upstream interpolation”, ''Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng''., '''19''', p59. | ||
13) Patankar S.V., | 13) Patankar S.V., 1980, ''“Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow”'', Hemisphere Publishing Corporation, Taylor and Francis Group, New York. | ||
14) Spalding D.B, | 14) Patankar S.V., Spalding D.B., 1972, “A Calculation Procedure of Heat, Mass and Momentum transfer in Three-Dimensional Parabolic Flows”, ''Int J. Heat and Mass Transfer'', '''15''', p1787. | ||
15) Spalding D.B, 1967, “Heat Transfer from Turbulent Separated Flows”, ''J. Fluid Mechanics'', '''27''', p97. | |||
16) Yap, C.R., 1987, “Turbulent heat and momentum transfer in recirculating and impinging flows”, PhD Thesis, Dept of Mech. Eng., Faculty of Technology, University of Manchester. | |||
=='''Figures'''== | =='''Figures'''== | ||
| Line 128: | Line 133: | ||
<math>\frac{D\tilde{\varepsilon}}{D{t}} = \frac{\partial}{\partial x_{j}}\left[{(\nu + \nu_{t}/\sigma_{\varepsilon})} \frac{\partial\tilde{\varepsilon}}{\partial x_{j}}\right] + c_\varepsilon | <center><math> | ||
\frac{D\tilde{\varepsilon}}{D{t}} = \frac{\partial}{\partial x_{j}}\left[{(\nu + \nu_{t}/\sigma_{\varepsilon})} \frac{\partial\tilde{\varepsilon}}{\partial x_{j}}\right] + c_{\varepsilon 1} \frac{\tilde{\varepsilon}}{k} {(P_k + G_k)} - c_{\varepsilon 2} f_2 \frac{\tilde{\varepsilon}^2}{k} + 2\nu\nu_{t}\left(\frac{\partial^2 U_{i}}{\partial x_{j}\partial x_k}\right)^2 | |||
</math></center> | |||
| Line 134: | Line 141: | ||
where the production rates of turbulent kinetic energy due to shear and buoyancy are: | where the production rates of turbulent kinetic energy due to shear and buoyancy are: | ||
<math> | |||
<center><math> | |||
P_k = -\overline{u_{i}u_{j}} \frac{\partial U_{i}}{\partial x_{j}}\qquad\text{and}\qquad | |||
G_k = -\beta g_i\overline{u_i\theta} | |||
</math></center> | |||
The turbulent viscosity is then calculated as: | The turbulent viscosity is then calculated as: | ||
<math>\nu_{t} = c_{\mu} f_{\mu}\frac{ | <center><math> | ||
\nu_{t} = c_{\mu} f_{\mu}\frac{k^2}{\varepsilon} | |||
</math></center> | |||
The stresses and turbulent heat fluxes are modelled as: | |||
<center><math> | |||
\overline{u_{i}u_{j}} = \frac{2}{3}k\delta_{ij} - \nu_{t}\left(\frac{\partial U_{i}}{\partial x_{j}} + \frac{\partial U_{j}}{\partial x_{i}}\right)\qquad\text{and}\qquad | |||
\overline{u_{i}\theta} = -\frac{\nu_{t}}{\sigma_{t}}\frac{\partial T}{\partial x_{i}} | |||
</math></center> | |||
and | The various constants and functions appearing in the model are: | ||
<center><math> | |||
c_{\mu} = 0.09 c_{\varepsilon 1} = 1.44\qquad | |||
c_{\varepsilon 2} = 1.92\qquad | |||
\sigma_{\varepsilon} = 1.3\qquad | |||
\sigma_{t} = 0.9 | |||
</math></center> | |||
<math>f_{\mu} = exp\left[\frac{-3.4}{{(1 + Re_{t}/50)}^2}\right]f_2 = 1-0.3 exp {(-Re^2_{t})}Re_{t} = \frac{ | <center><math> | ||
f_{\mu} = \exp\left[\frac{-3.4}{{(1 + Re_{t}/50)}^2}\right]\qquad | |||
f_2 = 1-0.3 \exp {(-Re^2_{t})}\qquad | |||
Re_{t} = \frac{k}{\nu\varepsilon} | |||
</math></center> | |||
=='''Appendix B'''== | =='''Appendix B'''== | ||
| Line 167: | Line 191: | ||
The standard wall function employs the log-laws: | The standard wall function employs the log-laws: | ||
<math>U | |||
<center><math> | |||
U^{*} = \frac{1}{\kappa}log {(E^{*} y^{*})}\qquad\qquad | |||
T^{*} = \sigma_{t}{(U^{*} + P^{*})} | |||
</math></center> | |||
where | where | ||
<math>U\ | <center><math> | ||
U^{*} = \frac{U k^\frac{1}{2}}{\nu}\qquad\qquad | |||
T^{*} = \rho C_{p}k^\frac{1}{2} \frac{(T_{w}-T)}{q_w}\qquad\qquad | |||
y^{*} = \frac{yk^\frac{1}{2}}{\nu} | |||
</math></center> | |||
and | and | ||
< | <center><math> | ||
P^{*} = 9.24\left[{\left(\frac{Pr}{s_t}\right)}^\frac{3}{4}-1\right] | |||
\left[1+0.28e^{-0.007\frac{Pr}{s_t}}\right]c_m^{-\frac{1}{4}}\qquad | |||
E^{*}=9.79\qquad\kappa=0.41\qquad\sigma_t=0.9 | |||
</math></center> | |||
In solving the ''k'' equation over the near-wall cell, the generation and dissipation terms are replaced by cell-averaged values, defined as | |||
<center><math> | |||
\overline{P_{\kappa}} = \frac{s^2_{w}}{\kappa{c}^{1/2}_{\mu}\rho k^{1/2}_{p} Y_{n}} \log\left(\frac{y_n}{y_\nu}\right) | |||
</math></center> | |||
<center><math> | |||
\overline{\varepsilon} = \frac{1}{y_{n}}\left[\frac{2{\mu k}_{p}}{y_{\nu}} + \frac{k^{3/2}_{p}}{c_{l}} \log \left(\frac{y_n}{y_\nu}\right)\right] | |||
</math></center> | |||
and the dissipation rate at the near-wall node is prescribed as | |||
<math>\varepsilon_{p} = \ | <center><math> | ||
\varepsilon_{p} = \frac{k^{3/2}_p}{c_l y_p} | |||
</math></center> | |||
=='''Appendix C'''== | =='''Appendix C'''== | ||
Latest revision as of 16:16, 11 February 2017
Downward flow in a heated annulus
Application Challenge 3-11 © copyright ERCOFTAC 2004
Comparison of Test data and CFD
The CFD explorations have brought out several important features relevant to the prediction of vertically downward flows through an annulus with a heated core tube.
• The study of Guy et al (1999) has shown that these annular flows (with the possible exception of very low Reynolds number cases) can be treated as axisymmetric, and that for water flows it is important to include the variation of molecular properties with temperature.
• Where buoyant effects are significant the computational studies have highlighted the need for an accurate modeling of the near-wall sublayer. The usual form of wall functions, based on a universal logarithmic wall law, do not account for these buoyancy effects and hence fail to predict the enhancement of heat transfer as the buoyancy parameter is increased.
• The analytical wall function, which accounts for buoyant forces within the viscous sublayer and mimics the effects of changes in the viscous sublayer thickness, returns results in generally good agreement with the data. It thus provides an economic alternative to low-Reynolds-number models, which would otherwise be needed in order to resolve accurately the near-wall region of these annular flows
.
• The present calculations have not included a lengthscale correction term in the ε equation. Earlier computations showed such a term to have some influence, particularly at high heat loadings. Further calculations using the present scheme under such conditions, particularly when reverse flow may occur, should therefore also include a correction of this form.
References
1) Cotton, M.A., Jackson, J.D., 1987, “Calculation of Turbulent Mixed Convection in a Vertical Tube using a Low-Reynolds-Number k-ε turbulence model”, Proc. 6th Turbulent Shear Flows Symposium, Toulouse, France.
2) Gerasimov A.V., 2002, “CFD Quality and Trust: Develoment and Validation of an Analytical Wall-Function Strategy for Modelling Forced, Mixed and Natural Convection Flows”, Report PM/GNSR/5106, Department of Mechanical, Aerospace & Manufacturing Engineering, UMIST.
3) Guy A., Iacovides H., Launder B.E., 1999, “Study of Downward Water Flow in a Heated Annulus, Phase 2”, Technical Report HTH/GNSR/5032, Department of Mechanical Engineering, UMIST.
4) Huang P.G., Leschziner M.A., 1983, “An Introduction and Guide to the Computer Code TEAM”, Report TFD/83/9/(R), Thermofluids Division, Department of Mechanical Engineering, UMIST.
5) Ince, N.Z., Launder, B.E., 1989, “On the Computation of Buoyancy-Driven Turbulent Flows in Rectangular Enclosures”, Int. J. Heat and Fluid Flow, 10, 110-117.
6) Jackson, J.D., Hall, W.B., 1979, “Influences of Buoyancy on Heat Transfer to Fluids Flowing in Vertical Tubes under Turbulent Conditions”, In Turbulent Forced Convection in Channels and Bundles Theory and Applications to Heat Exchangers and Nuclear Reactors, (eds. S. Kakac & D.B. Spalding), Vol 2, pp 613-640.
7) Jackson J.D., He S., Xu Z., Wu T., 2000, “CFD Quality and Trust – Generic Studies of Thermal Convection”, Technical Report HTH/GNSR/5029, School of Engineering, Univeristy of Manchester.
8) J.D. Jackson, Zeyuan Xu and Tian-Hua Wu, 2003, "On the influence of buoyancy on turbulence production and effectiveness of heat transfer in vertical flows", Turbulence, Heat and Mass Transfer 4 (published by Begell House, and edited by K. Hanjalic, Y. Nagano and M.J. Tummers), pp 837-844, Proceedings of the 4th International THMT Symposium, Antalya, Turkey, 12th - 17th October 2003.
9) Jones, W.P., Launder, B.E., 1972, “The Prediction of Laminarization with a Two-Equation Model of Turbulence”, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 15, 301-314.
10) Launder B.E., Sharma B.I., 1974, “Application of the Energy-Dissipation Model of Turbulence to the Calculation of Flow Near a Spinning Disc”, Letters in Heat and Mass Transfer, 1, pp131-138 .
11) Launder, B.E., 1986, “Low-Reynolds-Number Turbulence near Walls”, Report TFD/86/4, Dept of Mechanical Engineering, UMIST.
12) Leonard B.P., 1979, “A stable and accurate convective modeling procedure based on quadratic upstream interpolation”, Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng., 19, p59.
13) Patankar S.V., 1980, “Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow”, Hemisphere Publishing Corporation, Taylor and Francis Group, New York.
14) Patankar S.V., Spalding D.B., 1972, “A Calculation Procedure of Heat, Mass and Momentum transfer in Three-Dimensional Parabolic Flows”, Int J. Heat and Mass Transfer, 15, p1787.
15) Spalding D.B, 1967, “Heat Transfer from Turbulent Separated Flows”, J. Fluid Mechanics, 27, p97.
16) Yap, C.R., 1987, “Turbulent heat and momentum transfer in recirculating and impinging flows”, PhD Thesis, Dept of Mech. Eng., Faculty of Technology, University of Manchester.
Figures
Figure 4: Variation of Nusselt number and temperature along the heated inner wall for Re=6000, Bo=0.22.
Figure 5: Variation of Nusselt number and temperature along the heated inner wall for Re=6000, Bo=0.78.
Figure 6: Variation of Nusselt number and temperature along the heated inner wall for Re=4000, Bo=0.83.
Figure 7: Variation of Nusselt number and temperature along the heated inner wall for Re=4000, Bo=2.89.
Figure 8: Profiles of mean vertical velocity across the annular gap at a streamwise position x/deff=35.9. Upper graph: unheated case; Lower graph: buoyant case at Re=4000, Bo=2.89.
Figure 9: Normalized Mean temperature and vertical velocity profiles close to the inner heated wall at x/deff=35.9 for the buoyant case at Re=4000, Bo=2.89. (Position of main grid nodes is indicated by symbols on the wall function solutions).
Acknowledgement
This work was funded under the HSE Generic Nuclear Safety Research programme and is published with the permission of the UK Nuclear Industry Management Committee (IMC). The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial assistance provided for this investigation. The Manchester University experiments were carried out under the terms of the research Contract entitled ‘CFD Quality and Trust – Generic Studies of Thermal Convection’. The UMIST computational studies were carried out under the terms of the research Contract entitled ‘CFD Quality and Trust – Model Evaluation, Refinement and Application Advice’.
Appendix A
APPENDIX A: LRN MODEL (Low Reynolds Number k-ε Model)
The model of Launder & Sharma employs transport equations for the turbulent kinetic energy and its dissipation rate, and includes effects of molecular viscosity, allowing it to be applied across the viscous sublayer to the wall.
The equations for the turbulent energy and modified dissipation rate are:
where the production rates of turbulent kinetic energy due to shear and buoyancy are:
The turbulent viscosity is then calculated as:
The stresses and turbulent heat fluxes are modelled as:
The various constants and functions appearing in the model are:
Appendix B
APPENDIX B: StWF (Standard Wall Function)
The standard wall function employs the log-laws:
where
and
In solving the k equation over the near-wall cell, the generation and dissipation terms are replaced by cell-averaged values, defined as
and the dissipation rate at the near-wall node is prescribed as
Appendix C
APPENDIX C: AWF (Algebraic Wall Function)
Appendix D
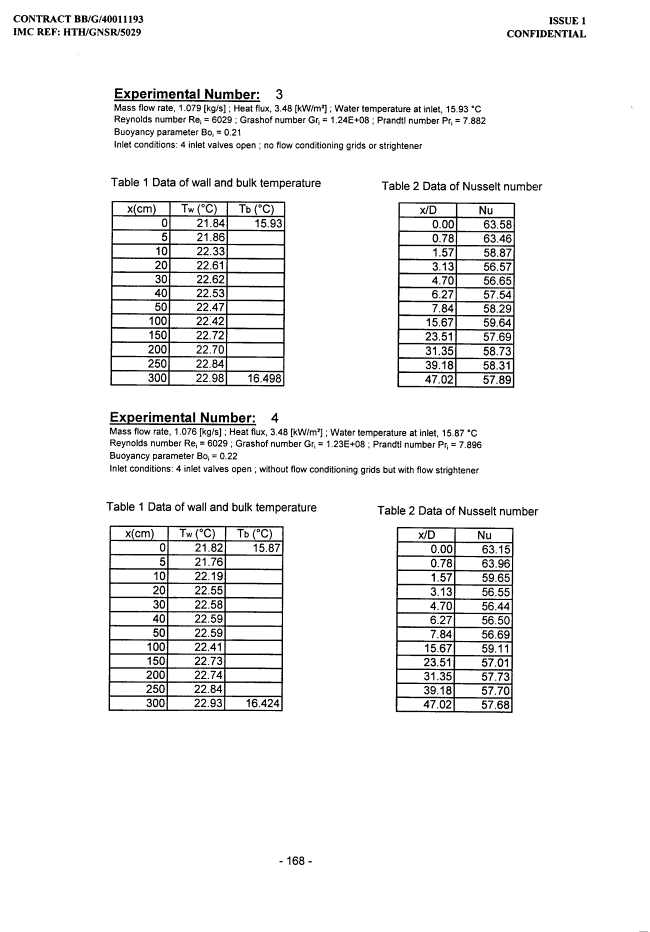
APPENDIX D: Experimental Temperature and Heat Transfer Results
Appendix E
APPENDIX E: Experimental Conditions and Heat Transfer Results
© copyright ERCOFTAC 2004
Contributors: Mike Rabbitt - British Energy
Site Design and Implementation: Atkins and UniS







![{\displaystyle {\frac {Dk}{D{t}}}={\frac {\partial }{\partial x_{j}}}\left[{(\nu +\nu _{t})}{\frac {\partial k}{\partial x_{j}}}\right]+P_{k}+G_{k}-{\tilde {\varepsilon }}-2\nu \left({\frac {\partial {\sqrt {k}}}{\partial x_{j}}}\right)^{2}}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2e65fb3235527a048026e0a5181bb5c5cabeed5b)
![{\displaystyle {\frac {D{\tilde {\varepsilon }}}{D{t}}}={\frac {\partial }{\partial x_{j}}}\left[{(\nu +\nu _{t}/\sigma _{\varepsilon })}{\frac {\partial {\tilde {\varepsilon }}}{\partial x_{j}}}\right]+c_{\varepsilon 1}{\frac {\tilde {\varepsilon }}{k}}{(P_{k}+G_{k})}-c_{\varepsilon 2}f_{2}{\frac {{\tilde {\varepsilon }}^{2}}{k}}+2\nu \nu _{t}\left({\frac {\partial ^{2}U_{i}}{\partial x_{j}\partial x_{k}}}\right)^{2}}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2658122f254d333675310b2fbf7fe0916bfc9cf1)




![{\displaystyle f_{\mu }=\exp \left[{\frac {-3.4}{{(1+Re_{t}/50)}^{2}}}\right]\qquad f_{2}=1-0.3\exp {(-Re_{t}^{2})}\qquad Re_{t}={\frac {k}{\nu \varepsilon }}}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/43095d119e4a5a46e86c9768d8173e487bc842ef)


![{\displaystyle P^{*}=9.24\left[{\left({\frac {Pr}{s_{t}}}\right)}^{\frac {3}{4}}-1\right]\left[1+0.28e^{-0.007{\frac {Pr}{s_{t}}}}\right]c_{m}^{-{\frac {1}{4}}}\qquad E^{*}=9.79\qquad \kappa =0.41\qquad \sigma _{t}=0.9}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0232dda5374fcb9ee77607cb522ae0e80df9abd3)

![{\displaystyle {\overline {\varepsilon }}={\frac {1}{y_{n}}}\left[{\frac {2{\mu k}_{p}}{y_{\nu }}}+{\frac {k_{p}^{3/2}}{c_{l}}}\log \left({\frac {y_{n}}{y_{\nu }}}\right)\right]}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/789bc47f9ae38366131828130c30e132dc6a7bfd)