UFR 4-05 Description: Difference between revisions
David.Fowler (talk | contribs) (New page: {{UFR|front=UFR 4-05|description=UFR 4-05 Description|references=UFR 4-05 References|testcase=UFR 4-05 Test Case|evaluation=UFR 4-05 Evaluation|qualityreview=UFR 4-05 Quality Review|bestp...) |
m (Dave.Ellacott moved page SilverP:UFR 4-05 Description to UFR 4-05 Description over redirect) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{UFR|front=UFR 4-05|description=UFR 4-05 Description|references=UFR 4-05 References|testcase=UFR 4-05 Test Case|evaluation=UFR 4-05 Evaluation|qualityreview=UFR 4-05 Quality Review|bestpractice=UFR 4-05 Best Practice Advice|relatedACs=UFR 4-05 Related ACs}} | {{UFR|front=UFR 4-05|description=UFR 4-05 Description|references=UFR 4-05 References|testcase=UFR 4-05 Test Case|evaluation=UFR 4-05 Evaluation|qualityreview=UFR 4-05 Quality Review|bestpractice=UFR 4-05 Best Practice Advice|relatedACs=UFR 4-05 Related ACs}} | ||
| Line 19: | Line 18: | ||
Three main flow patterns are potential sources of losses in turbomachinery. These are: | Three main flow patterns are potential sources of losses in turbomachinery. These are: | ||
*The passage vortex, which is generated by the interaction of the pressure gradient and the boundary layers near the solid walls. | |||
*The horseshoe vortex, which is generated by the interaction of the boundary layers on the end walls with a leading edge when the flow is curved by blades. This vortex starts at the leading edge near the end walls and develops in the inter-blade passage. | |||
*The wake, which is the lower velocity flow generated behind a blade. | |||
The two kinds of vortex and the wake often interact to form loss cores inside the flow behind the blade passage. The correct simulation of the losses is of course of great importance for who wants to predict the efficiency of his machine. Thus, the CFD simulations of such flows must capture the different vortex structure with high precision. | The two kinds of vortex and the wake often interact to form loss cores inside the flow behind the blade passage. The correct simulation of the losses is of course of great importance for who wants to predict the efficiency of his machine. Thus, the CFD simulations of such flows must capture the different vortex structure with high precision. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 26: | ||
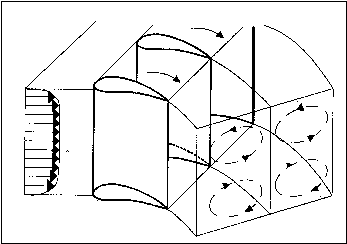
The physics of the underlying flow regime of a '''curved passage flow''' is governed by the interaction of the pressure gradient linked to the curvature of the main flow with the non-uniform flow (for instance due to boundary layers on solid walls). The flow, moving slower in the boundary layers, is pushed from the pressure side to the suction side, leading to an overturning in the end-wall regions. This gives rise to stream-wise vorticity generating an end-wall vortex in the curved passage (as illustrated on Figure 1:). It should be pointed out that the basic mechanics of this secondary flow generation is '''inviscid'''. Furthermore, due to the presence of a rounded leading edge, horseshoe vortices are also generated, which merge with the passage vortices. | The physics of the underlying flow regime of a '''curved passage flow''' is governed by the interaction of the pressure gradient linked to the curvature of the main flow with the non-uniform flow (for instance due to boundary layers on solid walls). The flow, moving slower in the boundary layers, is pushed from the pressure side to the suction side, leading to an overturning in the end-wall regions. This gives rise to stream-wise vorticity generating an end-wall vortex in the curved passage (as illustrated on Figure 1:). It should be pointed out that the basic mechanics of this secondary flow generation is '''inviscid'''. Furthermore, due to the presence of a rounded leading edge, horseshoe vortices are also generated, which merge with the passage vortices. | ||
[[Image:UFR4-05.gif|centre|thumb|347px|'''Figure 1.''' Passage vortex (From D. Japikse and N.C. Baines, 1997. « Introduction to Turbomachinery », Publishers: Concepts ETI, Inc. and Oxford University Press).]] | |||
[[Image: | |||
| | |||
The correct representation of this flow regime is of importance because: | The correct representation of this flow regime is of importance because: | ||
*It induces extra losses. | |||
*It leads to significant tri-dimensional flow effects with 3D separation on the blade suction side. | |||
*It induces a non-uniform heat transfer on the blade and end-wall surfaces and has a strong influence on the blade film cooling. | |||
*It affects the blade lifetime because of enhanced thermal and mechanical stresses. | |||
*It has an influence on the turbine stage work output. | |||
*It has an impact on downstream blade row efficiency due to an enhanced non-uniformity of the exit flow. | |||
This flow regime is influenced by numerous factors such as the blade shape, the pitch-chord ratio, the aspect ratio, the Mach number, and the inlet boundary layer thickness. Owing to its importance in turbomachinery design and to its interaction with other secondary motions, an excessive amount of work has been done on this flow regime. Therefore, a full and concise review of the literature on this UFR is far from trivial and will not be conducted here. | This flow regime is influenced by numerous factors such as the blade shape, the pitch-chord ratio, the aspect ratio, the Mach number, and the inlet boundary layer thickness. Owing to its importance in turbomachinery design and to its interaction with other secondary motions, an excessive amount of work has been done on this flow regime. Therefore, a full and concise review of the literature on this UFR is far from trivial and will not be conducted here. | ||
| Line 61: | Line 43: | ||
== Review of UFR studies and choice of test case == | == Review of UFR studies and choice of test case == | ||
The selected UFR study is described in the AGARD Advisory Report 355. This report called | The selected UFR study is described in the AGARD Advisory Report 355. This report called “CFD Validation for Propulsion System Components” compares numerical results from a large panel of solvers to the experiment for the NASA rotor 37 and for the DLR turbine stator. | ||
The '''DLR turbine stator''' is the test case discussed in the present documentation. It has been selected for this UFR because: | The '''DLR turbine stator''' is the test case discussed in the present documentation. It has been selected for this UFR because: | ||
* It is a representative example of turning and confined accelerating flow. | |||
* The program of this test was carried out in a well-developed test installation operated by an experienced research group. The measurements were performed with different proven instrumentation and data acquisition methods. | |||
* A wide range of experimental data is available. | |||
* It has already been used in a CFD validation and comparison exercise. | |||
* The studied turbine stator is the product of proven design methods and can be seen as a relevant example for many turbine flows. | |||
According to this report | According to this report “Transition predictions were not thought to be important for the test cases chosen by the Working Group”, therefore no special treatment of transition is required to perform this test case. | ||
<font size="-2" color="#888888">© copyright ERCOFTAC 2004</font><br /> | <font size="-2" color="#888888">© copyright ERCOFTAC 2004</font><br /> | ||
| Line 85: | Line 67: | ||
{{UFR|front=UFR 4-05|description=UFR 4-05 Description|references=UFR 4-05 References|testcase=UFR 4-05 Test Case|evaluation=UFR 4-05 Evaluation|qualityreview=UFR 4-05 Quality Review|bestpractice=UFR 4-05 Best Practice Advice|relatedACs=UFR 4-05 Related ACs}} | {{UFR|front=UFR 4-05|description=UFR 4-05 Description|references=UFR 4-05 References|testcase=UFR 4-05 Test Case|evaluation=UFR 4-05 Evaluation|qualityreview=UFR 4-05 Quality Review|bestpractice=UFR 4-05 Best Practice Advice|relatedACs=UFR 4-05 Related ACs}} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:09, 12 February 2017
Curved passage flow
Underlying Flow Regime 4-05 © copyright ERCOFTAC 2004
Description
Introduction
Three main flow patterns are potential sources of losses in turbomachinery. These are:
- The passage vortex, which is generated by the interaction of the pressure gradient and the boundary layers near the solid walls.
- The horseshoe vortex, which is generated by the interaction of the boundary layers on the end walls with a leading edge when the flow is curved by blades. This vortex starts at the leading edge near the end walls and develops in the inter-blade passage.
- The wake, which is the lower velocity flow generated behind a blade.
The two kinds of vortex and the wake often interact to form loss cores inside the flow behind the blade passage. The correct simulation of the losses is of course of great importance for who wants to predict the efficiency of his machine. Thus, the CFD simulations of such flows must capture the different vortex structure with high precision.
The physics of the underlying flow regime of a curved passage flow is governed by the interaction of the pressure gradient linked to the curvature of the main flow with the non-uniform flow (for instance due to boundary layers on solid walls). The flow, moving slower in the boundary layers, is pushed from the pressure side to the suction side, leading to an overturning in the end-wall regions. This gives rise to stream-wise vorticity generating an end-wall vortex in the curved passage (as illustrated on Figure 1:). It should be pointed out that the basic mechanics of this secondary flow generation is inviscid. Furthermore, due to the presence of a rounded leading edge, horseshoe vortices are also generated, which merge with the passage vortices.
The correct representation of this flow regime is of importance because:
- It induces extra losses.
- It leads to significant tri-dimensional flow effects with 3D separation on the blade suction side.
- It induces a non-uniform heat transfer on the blade and end-wall surfaces and has a strong influence on the blade film cooling.
- It affects the blade lifetime because of enhanced thermal and mechanical stresses.
- It has an influence on the turbine stage work output.
- It has an impact on downstream blade row efficiency due to an enhanced non-uniformity of the exit flow.
This flow regime is influenced by numerous factors such as the blade shape, the pitch-chord ratio, the aspect ratio, the Mach number, and the inlet boundary layer thickness. Owing to its importance in turbomachinery design and to its interaction with other secondary motions, an excessive amount of work has been done on this flow regime. Therefore, a full and concise review of the literature on this UFR is far from trivial and will not be conducted here.
Since this underlying flow regime focuses on accelerating passage flow, the related secondary flows will be weak compared to decelerating flow. Furthermore, this study will mainly focus on the influence of the mesh and the turbulence model onto the underlying flow regime.
Review of UFR studies and choice of test case
The selected UFR study is described in the AGARD Advisory Report 355. This report called “CFD Validation for Propulsion System Components” compares numerical results from a large panel of solvers to the experiment for the NASA rotor 37 and for the DLR turbine stator.
The DLR turbine stator is the test case discussed in the present documentation. It has been selected for this UFR because:
- It is a representative example of turning and confined accelerating flow.
- The program of this test was carried out in a well-developed test installation operated by an experienced research group. The measurements were performed with different proven instrumentation and data acquisition methods.
- A wide range of experimental data is available.
- It has already been used in a CFD validation and comparison exercise.
- The studied turbine stator is the product of proven design methods and can be seen as a relevant example for many turbine flows.
According to this report “Transition predictions were not thought to be important for the test cases chosen by the Working Group”, therefore no special treatment of transition is required to perform this test case.
© copyright ERCOFTAC 2004
Contributors: Nouredine Hakimi - NUMECA International